User and collaboration
Sign up and log in
Potato supports self-registration by default. A new user can register for the annotation task by navigating to the annotation server, then selecting \"Create your account\".
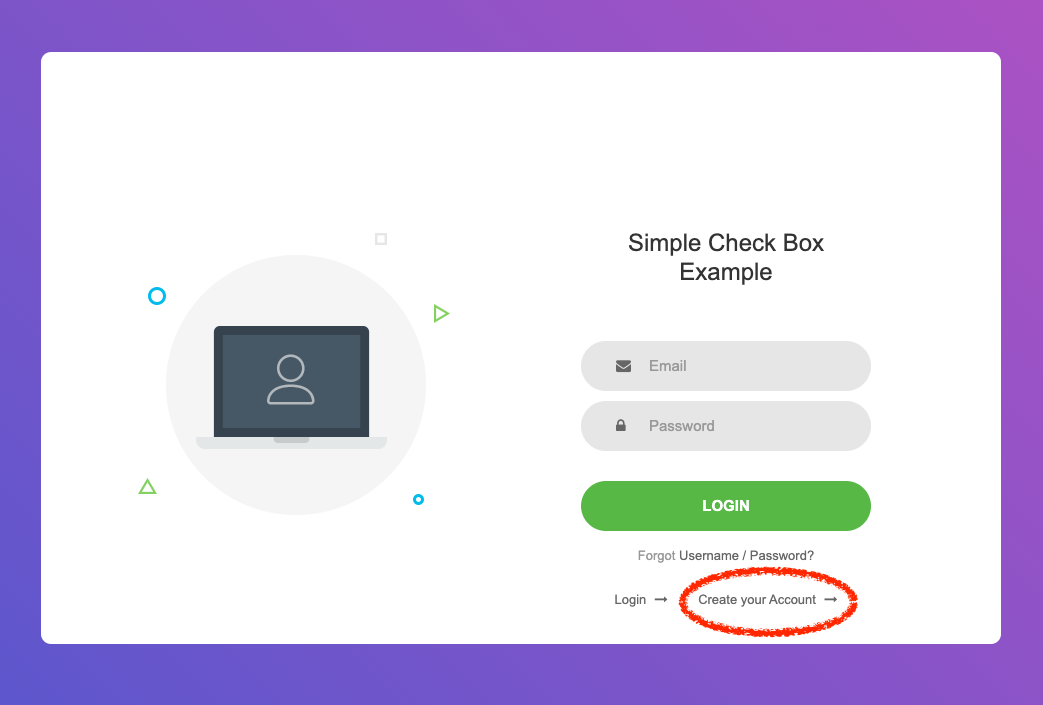
After creating an account, you can log in with the email and password used in the account creation step.
Set up authorized users
Sometimes you might only allow a short list of users to sign up.
All you need to do is set allow_all_users: False and add a list of authorized
emails to authorized_users. Other users will not be allowed to sign up.
"user_config": {
"allow_all_users": False,
"authorized_users": ["hello@123.com", "good@354.com"],
},
Direct login with URL argument
Potato also supports direct login through URL arguments, for example: http://localhost:8000/?PROLIFIC_PID=user
You could setup direct login in the YAML configuration file (example):
#defining the ways annotators entering the annotation system
"login": {
"type": 'url_direct', #can be 'password' or 'url_direct'
"url_argument": 'PROLIFIC_PID' # when the login type is set to 'url_direct', 'url_argument' must be setup for a direct url argument login
},
You can also use a list of url_arguments, for example
#defining the ways annotators entering the annotation system
"login": {
"type": 'url_direct', #can be 'password' or 'url_direct'
"url_argument": ['PROLIFIC_PID','STUDY_ID','SESSION_ID'] # when the login type is set to 'url_direct', 'url_argument' must be setup for a direct url argument login
},
In this setting, the annotation folder for each user will be named with the concatenation of all the url argument values
Collaboration under local network
If you do not want to expose the annotation app globally, Potato serves to the local area network by default. You can access the Potato instance through the local IP address of the server.
On Linux machines, you can determine the local IP by running
hostname -I